Word Search
Word Search:
Given an m x n grid of characters board and a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example 1:
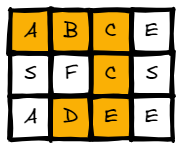
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
Output: true
Example 2:
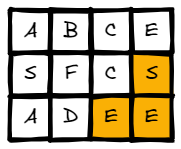
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
Output: true
Example 2:
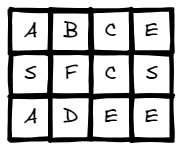
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
Output: false
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15boardandwordconsists of only lowercase and uppercase English letters.
Try this Problem on your own or check similar problems:
Solution:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
for(int i = 0; i < board.length; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; ++j){
if(helper(board, i, j, 0, word)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean helper(char[][] board, int x, int y, int index, String word){
if(index == word.length()) return true;
if(x < 0 || x == board.length || y < 0 || y == board[0].length || board[x][y] != word.charAt(index)){
return false;
}
board[x][y] = '#';
boolean exist = helper(board, x + 1, y, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x, y + 1, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x - 1, y, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x, y - 1, index + 1, word);
board[x][y] = word.charAt(index);
return exist;
}
}
/**
* @param {character[][]} board
* @param {string} word
* @return {boolean}
*/
var exist = function (board, word) {
for (let i = 0; i < board.length; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < board[0].length; ++j) {
if (helper(board, i, j, 0, word)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
};
function helper(board, x, y, index, word) {
if (index === word.length) {
return true;
}
if (
x < 0 ||
x === board.length ||
y < 0 ||
y === board[0].length ||
board[x][y] !== word.charAt(index)
) {
return false;
}
board[x][y] = "#";
const exist =
helper(board, x + 1, y, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x, y + 1, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x - 1, y, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x, y - 1, index + 1, word);
board[x][y] = word.charAt(index);
return exist;
}
class Solution:
def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if self.helper(board, i, j, 0, word):
return True
return False
def helper(self, board: List[List[str]], x: int, y: int, index: int, word: str) -> bool:
if index == len(word):
return True
if x < 0 or x == len(board) or y < 0 or y == len(board[0]) or board[x][y] != word[index]:
return False
board[x][y] = '#'
exist = self.helper(board, x + 1, y, index + 1, word) \
or self.helper(board, x, y + 1, index + 1, word) \
or self.helper(board, x - 1, y, index + 1, word) \
or self.helper(board, x, y - 1, index + 1, word)
board[x][y] = word[index]
return exist
class Solution {
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].size(); ++j) {
if (helper(board, i, j, 0, word)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private:
bool helper(vector<vector<char>>& board, int x, int y, int index, string word) {
if (index == word.length()) {
return true;
}
if (x < 0 || x == board.size() || y < 0 || y == board[0].size() || board[x][y] != word[index]) {
return false;
}
board[x][y] = '#';
bool exist = helper(board, x + 1, y, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x, y + 1, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x - 1, y, index + 1, word) ||
helper(board, x, y - 1, index + 1, word);
board[x][y] = word[index];
return exist;
}
};
Time/Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(mn4^L)
- Space Complexity: O(L)
Explanation:
This is a standard DFS search in matrix with backtracking, the space complexity is the recursion stack where depth is equal to the length of the word L and at each level we have 4 directions to choose from (breadth/width of the recursions tree). The time complexity is O(m*n*4^L), the complexity for matrix traversal times the operation we do with each element in the matrix, in our case it's the recursive helper operation which goes L in depth and 4 in breadth. So how do we solve this problem?
We traverse the matrix starting for a good position (matching our first letter) and then we check if we can form the word from the grid adjacent characters. We have two base cases:
- Base case - when index is equal to the word length which means we found our word and we return
true. - When the current position is out-of-boundary or the character at the current position doesn't match the character at current word index, so we return
false.
We use special character # to mark the visited position in matrix and then check for the next index in the word (by moving down, right, up or left), if any of those scenario works out exist will be true, otherwise it will be false, so we can just return it as result of our helper operation. Before we do that, we must restore the value of the current position to its previous value (character at current index) essentially performing backtracking.