Reverse Linked List II
Reverse Linked List II:
Given the head of a singly linked list and two integers left and right where left <= right, reverse the nodes of the list from position left to position right, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
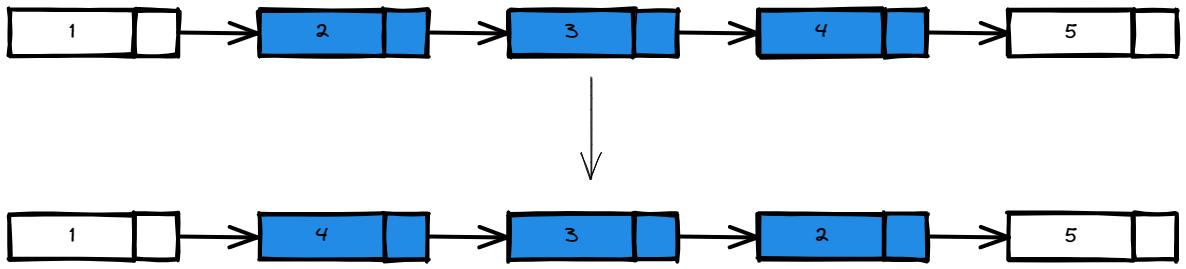
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
Output: [1,4,3,2,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
Output: [5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
n. 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
Try this Problem on your own or check similar problems:
Solution:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode iter = dummy, start = null;
for(int i = 0; i < left; ++i){
start = iter;
iter = iter.next;
}
for(int i = 0; i < right - left; ++i){
ListNode next = iter.next;
iter.next = next.next;
next.next = start.next;
start.next = next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} left
* @param {number} right
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var reverseBetween = function (head, left, right) {
let dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
let iter = dummy;
let start = null;
for (let i = 0; i < left; ++i) {
start = iter;
iter = iter.next;
}
for (let i = 0; i < right - left; ++i) {
let next = iter.next;
iter.next = next.next;
next.next = start.next;
start.next = next;
}
return dummy.next;
};
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: Optional[ListNode], left: int, right: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy = ListNode(-1, head)
iter = dummy
start = None
for i in range(left):
start = iter
iter = iter.next
for i in range(right - left):
next = iter.next
iter.next = next.next
next.next = start.next
start.next = next
return dummy.next
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) {
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode* iter = dummy;
ListNode* start = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < left; ++i) {
start = iter;
iter = iter->next;
}
for (int i = 0; i < right - left; ++i) {
ListNode* next = iter->next;
iter->next = next->next;
next->next = start->next;
start->next = next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
Time/Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
Explanation:
We first check with the interviewer if the left and right represent valid boundaries, in other words if the length of the list is greater than both left and right (and if left is always smaller than right). As always we create a dummy node which is pointing to the current head and we use it to return the head of the modified list as our final result return dummy.next. Other than that, we have two loops, the first one is trivial, we iterate over to the node representing the start of the sublist that will be reversed (input left), we also keep a reference to the previous element (element before the start of the sublist to be reversed) and we name it start. The second loop is the core of the algorithm, we iterate over right - left nodes. The right - left represents the number of next connections between nodes marked as left and right (and those next connections are the ones we must redirect, to reverse the sublist). Each iteration we have three steps (e.g. list start -> 1 (iter) -> 2 (next) -> 3):
- we move the
iterforward (bubble out to the end) (the node1will be moved one place to the right each iteration, ending in the last position after the last iteration) - redirect the next nodes pointer
nextto the whatever ourstartis pointing to (2 -> 1) - and finally making
startpoint to the next element in the sublist (start -> 2).