Sort List
Sort List:
Given the head of a linked list, return *the list after sorting it in ascending order*.
Example 1:
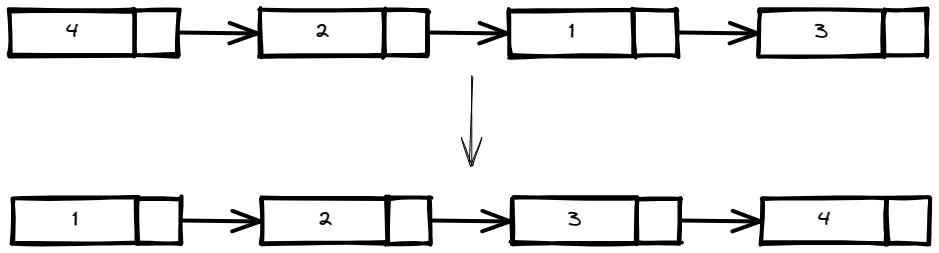
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
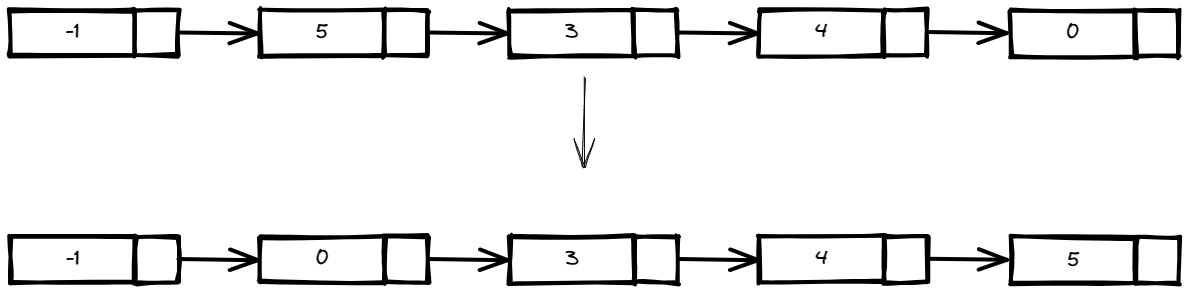
Example 2:
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 5 * 10^4]. -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
Try this Problem on your own or check similar problems:
Solution:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode slow = dummy, fast = dummy;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode secondHalfHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
ListNode firstHalfHead = sortList(head);
secondHalfHead = sortList(secondHalfHead);
return mergeTwoLists(firstHalfHead, secondHalfHead);
}
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null || list2 == null) return list1 == null ? list2 : list1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, null), curr = dummy;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val < list2.val){
curr.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
else{
curr.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
if(list1 != null || list2 != null){
curr.next = list1 != null ? list1 : list2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var sortList = function (head) {
if (head === null || head.next === null) return head;
const dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
let slow = dummy;
let fast = dummy;
while (fast !== null && fast.next !== null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
let secondHalfHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
let firstHalfHead = sortList(head);
secondHalfHead = sortList(secondHalfHead);
return mergeTwoLists(firstHalfHead, secondHalfHead);
};
function mergeTwoLists(list1, list2) {
if (list1 === null || list2 === null) return list1 === null ? list2 : list1;
const dummy = new ListNode(-1, null);
let curr = dummy;
while (list1 !== null && list2 !== null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
curr.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else {
curr.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
if (list1 !== null || list2 !== null) {
curr.next = list1 !== null ? list1 : list2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
dummy = ListNode(-1, head)
slow = dummy
fast = dummy
while fast is not None and fast.next is not None:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
secondHalfHead = slow.next
slow.next = None
firstHalfHead = self.sortList(head)
secondHalfHead = self.sortList(secondHalfHead)
return self.mergeTwoLists(firstHalfHead, secondHalfHead)
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1, list2):
if list1 is None or list2 is None:
return list1 if list1 is not None else list2
dummy = ListNode(-1, None)
curr = dummy
while list1 is not None and list2 is not None:
if list1.val < list2.val:
curr.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
else:
curr.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
curr = curr.next
if list1 is not None or list2 is not None:
curr.next = list1 if list1 is not None else list2
return dummy.next
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode* slow = dummy;
ListNode* fast = dummy;
while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* secondHalfHead = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
ListNode* firstHalfHead = sortList(head);
secondHalfHead = sortList(secondHalfHead);
return mergeTwoLists(firstHalfHead, secondHalfHead);
}
private:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
if (list1 == nullptr || list2 == nullptr) return list1 == nullptr ? list2 : list1;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1, nullptr);
ListNode* curr = dummy;
while (list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr) {
if (list1->val < list2->val) {
curr->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
} else {
curr->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
if (list1 != nullptr || list2 != nullptr) {
curr->next = list1 != nullptr ? list1 : list2;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
Time/Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(nlogn)
- Space Complexity: O(logn)
Explanation:
We already know how to merge lists together using the approach we implemented in Merge Two Sorted Lists so we can just use it here too as the second part of the mergesort process. To break the linked list into two parts (and keep on halving those halves recursively) we can use the slow and fast pointer approach, where the faster pointer is moving 1 node faster than the slower (double the speed), so when the fast arrives at the last element, the slow one will be at the middle. We can use this information because the slow pointer now has next set to the start of the second half of the linked list, while the first half starts at the original list head. To break those halves into two, and prevent infinite loop we do slow.next = null which breaks the connection between the halves. We recursively call the sortList on both halves and merge the two lists using our mergeTwoLists helper function. Note that space complexity here is O(logn) since we have recursion stack only contributing to it, but it is possible to reduce the space complexity down to constant O(1) if we turn this solution into iterative one. Notice that we're breaking the list down to sublists with only one node, then combining those into sorted sublists with two nodes and so on. We can use that information and start diving by some factor (e.g. first all 1-node size lists, than 2-nodes lists...) each time doubling the factor. We would also need to keep track on the tails of all those sublists and pointers showing to the next sublist we want to operate on. The code is given below:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
class Solution {
ListNode tail = new ListNode();
ListNode nextSubList = new ListNode();
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
int n = getCount(head);
ListNode start = head;
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
for (int size = 1; size < n; size = size * 2) {
tail = dummyHead;
while (start != null) {
if (start.next == null) {
tail.next = start;
break;
}
ListNode mid = split(start, size);
merge(start, mid);
start = nextSubList;
}
start = dummyHead.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
ListNode split(ListNode start, int size) {
ListNode midPrev = start;
ListNode end = start.next;
for (int index = 1; index < size && (midPrev.next != null || end.next != null); index++) {
if (end.next != null) {
end = (end.next.next != null) ? end.next.next : end.next;
}
if (midPrev.next != null) {
midPrev = midPrev.next;
}
}
ListNode mid = midPrev.next;
midPrev.next = null;
nextSubList = end.next;
end.next = null;
return mid;
}
void merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
ListNode newTail = dummyHead;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
newTail.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
newTail = newTail.next;
} else {
newTail.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
newTail = newTail.next;
}
}
newTail.next = (list1 != null) ? list1 : list2;
while (newTail.next != null) {
newTail = newTail.next;
}
tail.next = dummyHead.next;
tail = newTail;
}
int getCount(ListNode head) {
int cnt = 0;
ListNode ptr = head;
while (ptr != null) {
ptr = ptr.next;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var sortList = function (head) {
if (head === null || head.next === null) return head;
let n = getCount(head);
let start = head;
let dummyHead = new ListNode();
let tail = null;
let nextSubList = null;
for (let size = 1; size < n; size *= 2) {
tail = dummyHead;
while (start !== null) {
if (start.next === null) {
tail.next = start;
break;
}
let mid = split(start, size);
merge(start, mid);
start = nextSubList;
}
start = dummyHead.next;
}
return dummyHead.next;
};
function split(start, size) {
let midPrev = start;
let end = start.next;
for (
let index = 1;
index < size && (midPrev.next !== null || end.next !== null);
index++
) {
if (end.next !== null) {
end = end.next.next !== null ? end.next.next : end.next;
}
if (midPrev.next !== null) {
midPrev = midPrev.next;
}
}
let mid = midPrev.next;
midPrev.next = null;
nextSubList = end.next;
end.next = null;
return mid;
}
function merge(list1, list2) {
let dummyHead = new ListNode();
let newTail = dummyHead;
while (list1 !== null && list2 !== null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
newTail.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
newTail = newTail.next;
} else {
newTail.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
newTail = newTail.next;
}
}
newTail.next = list1 !== null ? list1 : list2;
while (newTail.next !== null) {
newTail = newTail.next;
}
tail.next = dummyHead.next;
tail = newTail;
}
function getCount(head) {
let cnt = 0;
let ptr = head;
while (ptr !== null) {
ptr = ptr.next;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
tail = ListNode()
nextSubList = ListNode()
def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
n = self.getCount(head)
start = head
dummyHead = ListNode()
tail = None
nextSubList = None
size = 1
while size < n:
tail = dummyHead
while start is not None:
if start.next is None:
tail.next = start
break
mid = self.split(start, size)
self.merge(start, mid)
start = nextSubList
start = dummyHead.next
size *= 2
return dummyHead.next
def split(self, start, size):
midPrev = start
end = start.next
for index in range(1, size):
if end.next is not None:
end = end.next.next if end.next.next is not None else end.next
if midPrev.next is not None:
midPrev = midPrev.next
mid = midPrev.next
midPrev.next = None
self.nextSubList = end.next
end.next = None
return mid
def merge(self, list1, list2):
dummyHead = ListNode()
newTail = dummyHead
while list1 is not None and list2 is not None:
if list1.val < list2.val:
newTail.next = list1
list1 = list1.next
newTail = newTail.next
else:
newTail.next = list2
list2 = list2.next
newTail = newTail.next
newTail.next = list1 if list1 is not None else list2
while newTail.next is not None:
newTail = newTail.next
self.tail.next = dummyHead.next
self.tail = newTail
def getCount(self, head):
cnt = 0
ptr = head
while ptr is not None:
ptr = ptr.next
cnt += 1
return cnt
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return head;
int n = getCount(head);
ListNode* start = head;
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();
tail = nullptr;
nextSubList = nullptr;
for (int size = 1; size < n; size *= 2) {
tail = dummyHead;
while (start != nullptr) {
if (start->next == nullptr) {
tail->next = start;
break;
}
ListNode* mid = split(start, size);
merge(start, mid);
start = nextSubList;
}
start = dummyHead->next;
}
ListNode* sortedHead = dummyHead->next;
delete dummyHead;
return sortedHead;
}
private:
ListNode* split(ListNode* start, int size) {
ListNode* midPrev = start;
ListNode* end = start->next;
for (int index = 1; index < size && (midPrev->next != nullptr || end->next != nullptr); index++) {
if (end->next != nullptr) {
end = end->next->next != nullptr ? end->next->next : end->next;
}
if (midPrev->next != nullptr) {
midPrev = midPrev->next;
}
}
ListNode* mid = midPrev->next;
midPrev->next = nullptr;
nextSubList = end->next;
end->next = nullptr;
return mid;
}
void merge(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode();
ListNode* newTail = dummyHead;
while (list1 != nullptr && list2 != nullptr) {
if (list1->val < list2->val) {
newTail->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
newTail = newTail->next;
} else {
newTail->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
newTail = newTail->next;
}
}
newTail->next = list1 != nullptr ? list1 : list2;
while (newTail->next != nullptr) {
newTail = newTail->next;
}
tail->next = dummyHead->next;
tail = newTail;
delete dummyHead;
}
int getCount(ListNode* head) {
int cnt = 0;
ListNode* ptr = head;
while (ptr != nullptr) {
ptr = ptr->next;
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
};