Rotate List
Rotate List:
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Example 1:
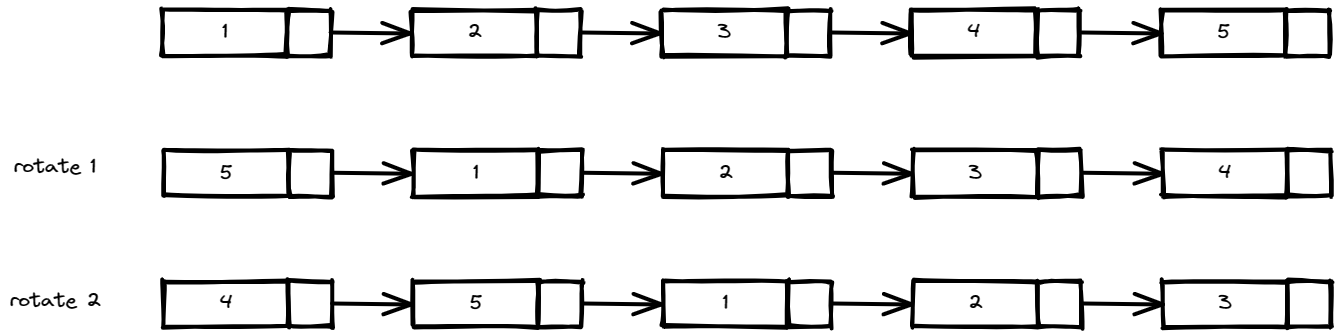
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
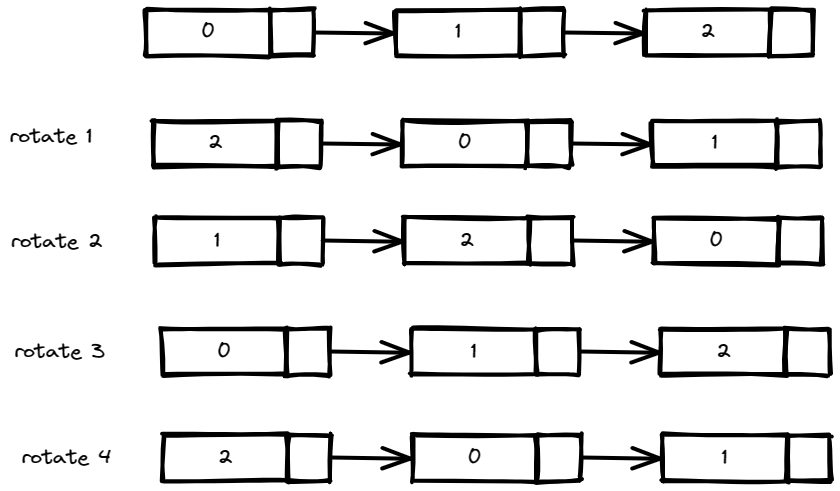
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4
Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500]. -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 10^9
Try this Problem on your own or check similar problems:
Solution:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if(head == null) return head;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head), iter = dummy.next, tail = null;
int listLength = 0;
while(iter != null){
++listLength;
tail = iter;
iter = iter.next;
}
int numberOfRotations = k % listLength;
if(numberOfRotations == 0) return head;
ListNode slow = dummy, fast = dummy;
while(numberOfRotations-->0){
fast = fast.next;
}
while(fast.next != null){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
ListNode newHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
tail.next = head;
return newHead;
}
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} head
* @param {number} k
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var rotateRight = function (head, k) {
if (head === null) return head;
const dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
let iter = dummy.next;
let tail = null;
let listLength = 0;
while (iter !== null) {
listLength++;
tail = iter;
iter = iter.next;
}
let numberOfRotations = k % listLength;
if (numberOfRotations === 0) return head;
let slow = dummy;
let fast = dummy;
while (numberOfRotations-- > 0) {
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next !== null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
const newHead = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
tail.next = head;
return newHead;
};
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def rotateRight(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None:
return head
dummy = ListNode(-1, head)
iter = dummy.next
tail = None
listLength = 0
while iter is not None:
listLength += 1
tail = iter
iter = iter.next
numberOfRotations = k % listLength
if numberOfRotations == 0:
return head
slow = dummy
fast = dummy
while numberOfRotations > 0:
fast = fast.next
numberOfRotations -= 1
while fast.next is not None:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
newHead = slow.next
slow.next = None
tail.next = head
return newHead
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if (head == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode* iter = dummy->next;
ListNode* tail = nullptr;
int listLength = 0;
while (iter != nullptr) {
listLength++;
tail = iter;
iter = iter->next;
}
int numberOfRotations = k % listLength;
if (numberOfRotations == 0) return head;
ListNode* slow = dummy;
ListNode* fast = dummy;
while (numberOfRotations-- > 0) {
fast = fast->next;
}
while (fast->next != nullptr) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
ListNode* newHead = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
tail->next = head;
return newHead;
}
};
Time/Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
Explanation:
We have three pieces to this code:
- First we calculate the length of the list by iterating until we reach
null. - We use list length to determine the number of rotations (if
k > listLength, e.g.k=4, listLength=3, after three rotations we will have the same list as if we had not rotations at all, so the only fourth rotation countsk % n). We know how to find the nth element from the end of the list using the approach we implemented in Remove Nth Node From End of List. That node will become the next head of the list afternrotations. - In the last piece we keep the reference to the
newHeadwhich we return as the result of our function. We also break the connection between the rotated part and the rest of the linked listslow.next = null. We connect the tail (the last node) to the non-rotated part of the list that will be shifted right bynplaces (number of rotations), while the firstnnodes of the list will be the rotated part (nodes fromnthnode to thetail).