Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Average of Levels in Binary Tree:
Given the root of a binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array. Answers within 10^-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:
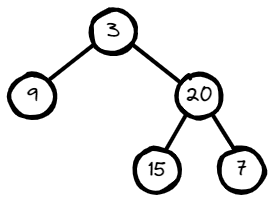
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
Explanation: The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3,
on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11.
Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
Example 2:
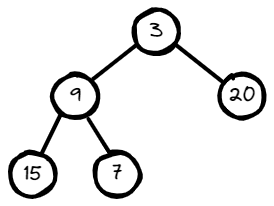
Input: root = [3,9,20,15,7]
Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 10^4]. -2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
Try this Problem on your own or check similar problems:
Solution:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
List<Double> result = new ArrayList<Double>();
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int size = q.size(), numberOfElements = size;
double sum = 0;
while(numberOfElements-->0){
TreeNode node = q.poll();
sum += node.val;
if(node.left != null){
q.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null){
q.add(node.right);
}
}
result.add(sum / size);
}
return result;
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var averageOfLevels = function (root) {
const q = [];
const result = [];
q.push(root);
while (q.length > 0) {
const size = q.length;
let numberOfElements = size;
let totalSum = 0;
while (numberOfElements > 0) {
const node = q.shift();
totalSum += node.val;
if (node.left) {
q.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right) {
q.push(node.right);
}
numberOfElements--;
}
result.push(totalSum / size);
}
return result;
};
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def averageOfLevels(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[float]:
q = deque()
result = []
q.append(root)
while q:
size = len(q)
numberOfElements = size
totalSum = 0
while numberOfElements > 0:
node = q.popleft()
totalSum += node.val
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
numberOfElements -= 1
result.append(totalSum / size)
return result
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
std::queue<TreeNode*> q;
std::vector<double> result;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
int numberOfElements = size;
double totalSum = 0;
while (numberOfElements-- > 0) {
TreeNode* node = q.front();
q.pop();
totalSum += node->val;
if (node->left) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
q.push(node->right);
}
}
result.push_back(totalSum / size);
}
return result;
}
};
Time/Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(n)
Explanation:
Classic BFS (Breadth-first search) of the tree. Since we use a queue the space complexity is linear O(n). To go over tree level by level we start by adding the root to the queue. Then each iteration of the outer loop we poll all the elements (current level).
For each polled element we check if it has left and right child, if it does we add them to the queue and they become the next level nodes. After each iteration of outer loop, we store the average in list and return the list as the final result.