Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Maximum Depth of Binary Tree:
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:
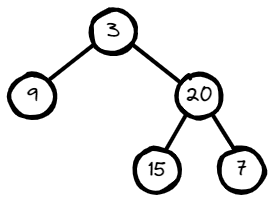
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2]
Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 10^4]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Try this Problem on your own or check similar problems:
Solution:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function (root) {
if (root === null) return 0;
let left = maxDepth(root.left);
let right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
};
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
left = self.maxDepth(root.left)
right = self.maxDepth(root.right)
return max(left, right) + 1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return std::max(left, right) + 1;
}
};
Time/Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(n)
Explanation:
Remember how we used BFS for the shortest path to leaf node (min depth) in Minimum Depth of Binary Tree, well in this case the we can use DFS since by the problem statement we have to find the longest root-to-leaf path so the optimization we did with BFS is not useful for this problem. The problem is trivial, we check left and right subtree depth and have a base case for root == null to start iterating back from the recursion stack. For each recursion call we just return the deeper subtree.