Symmetric Tree
Symmetric Tree:
Given the root of a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (i.e., symmetric around its center).
Example 1:
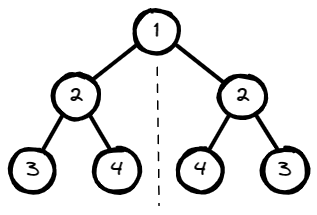
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
Output: true
Example 2:
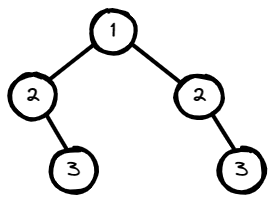
Input: root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
Output: false
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Try this Problem on your own or check similar problems:
Solution:
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root.left == null || root.right == null) return root.left == root.right;
return helper(root.left, root.right);
}
private boolean helper(TreeNode left, TreeNode right){
if(left == null || right == null) return left == right;
if(left.val != right.val) return false;
return helper(left.left, right.right) && helper(left.right, right.left);
}
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isSymmetric = function (root) {
if (root.left === null || root.right === null)
return root.left === root.right;
return helper(root.left, root.right);
};
function helper(left, right) {
if (left === null || right === null) return left === right;
if (left.val !== right.val) return false;
return helper(left.left, right.right) && helper(left.right, right.left);
}
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if root.left is None or root.right is None:
return root.left == root.right
return self.helper(root.left, root.right)
def helper(self, left, right):
if left is None or right is None:
return left == right
if left.val != right.val:
return False
return self.helper(left.left, right.right) and self.helper(left.right, right.left)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (root->left == nullptr || root->right == nullptr)
return root->left == root->right;
return helper(root->left, root->right);
}
private:
bool helper(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right) {
if (left == nullptr || right == nullptr)
return left == right;
if (left->val != right->val)
return false;
return helper(left->left, right->right) && helper(left->right, right->left);
}
};
Time/Space Complexity:
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Space Complexity: O(h)
Explanation:
We traverse all nodes leading to linear time complexity proportional to the number of nodes in the tree and since we have recursion stack up to the height of the tree, we have space complexity of O(h) where h is the height of the tree. We first check if both children of root are defined, if not we check if both are null to have a symmetry. We utilize the helper function that checks recursively if the subtrees are symmetric, by first checking if both subtrees are defined and have equal values. Then we check if the left child of left subtree is symmetric to the right child of right subtree and if right child of left subtree is symmetric to left child of right subtree. If both requirements are fulfilled, we know the subtrees are symmetric and we return true. If we want to check if tree is symmetric iteratively, we can use stack and mimic the recursion (getting the same time and space complexity):
- Java
- JavaScript
- Python
- C++
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root.left == null || root.right == null) return root.left == root.right;
Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<>();
s.push(root.right);
s.push(root.left);
while(s.size() > 1){
TreeNode left = s.pop();
TreeNode right = s.pop();
if((left == null || right == null) && left != right) return false;
if(left == null) continue;
if(left.val != right.val) return false;
s.push(right.left);
s.push(left.right);
s.push(right.right);
s.push(left.left);
}
return s.empty();
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isSymmetric = function (root) {
if (!root.left || !root.right) return root.left === root.right;
let s = [];
s.push(root.right);
s.push(root.left);
while (s.length > 1) {
let left = s.pop();
let right = s.pop();
if ((left === null || right === null) && left !== right) return false;
if (left === null) continue;
if (left.val !== right.val) return false;
s.push(right.left);
s.push(left.right);
s.push(right.right);
s.push(left.left);
}
return s.length === 0;
};
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isSymmetric(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> bool:
if not root.left or not root.right:
return root.left == root.right
s = []
s.append(root.right)
s.append(root.left)
while len(s) > 1:
left = s.pop()
right = s.pop()
if (left is None or right is None) and left is not right:
return False
if left is None:
continue
if left.val != right.val:
return False
s.append(right.left)
s.append(left.right)
s.append(right.right)
s.append(left.left)
return len(s) == 0
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root->left || !root->right) return root->left == root->right;
stack<TreeNode*> s;
s.push(root->right);
s.push(root->left);
while (s.size() > 1) {
TreeNode* left = s.top();
s.pop();
TreeNode* right = s.top();
s.pop();
if ((left == nullptr || right == nullptr) && left != right) return false;
if (left == nullptr) continue;
if (left->val != right->val) return false;
s.push(right->left);
s.push(left->right);
s.push(right->right);
s.push(left->left);
}
return s.empty();
}
};
Note that we put the nodes in reverse order of recursion calls in the stack since stack is LIFO (last in first out) data structure.